7.1 Sending queries to web services (Vizier, SkyBoT)¶
Retrieving data from Vizier¶
AsPyLib allows to send a simple “cone search” request to the Vizier service, and retrieve star positions and information from any catalog. To do it you only need to specify:
- a catalog
- a position (alpha, delta)
- a cone radius in arcmin, or a rectangular box size in arcmin x arcmin
To see how it works, the simplest way is to show an example. The script below retrieves all stars with magnitude smaller than 11, in an area of 7deg*10deg centered on the Pleiades, in Taurus.
from aspylib import astrometry, astro
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#------ retrieving information from Vizier ------
catalog = 'USNO-B1'
position = [56., 24.] #[alpha, delta] in degrees
conesize = [600., 420.] #[boxsize_alpha, boxsize_delta] in arcmin
constraint = 'B1mag<=11'
astrometry.send_query_vizier(catalog, position, conesize, constraint)
stars = astrometry.read_votable("vizier.xml")
#------ printing information --------------------
print
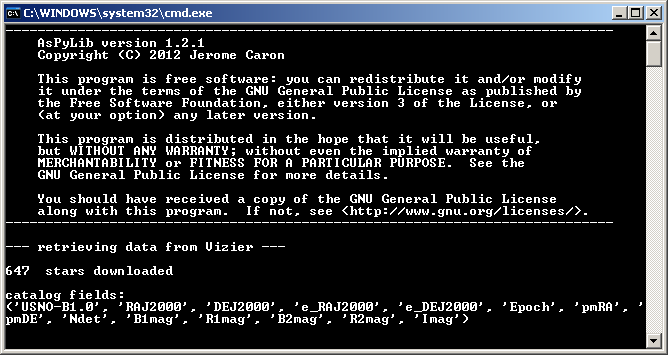
print len(stars)," stars downloaded"
print
print "catalog fields:"
print stars.dtype.names
#------ generating sky map ----------------------
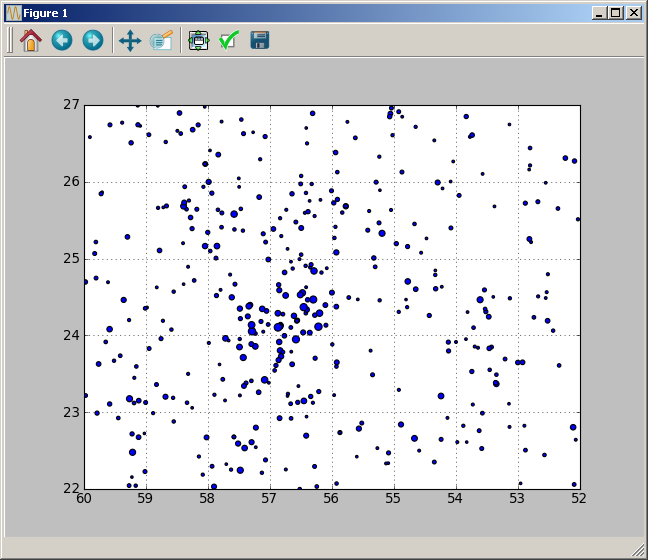
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(stars['RAJ2000'],stars['DEJ2000'],s=4*(12-stars['B1mag']))
plt.grid()
plt.xlim([52,60])
plt.ylim([22,27])
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xlim(ax.get_xlim()[::-1])
plt.show()
Then we get the following messages in the Python console:
And the following sky map is shown:
The first instruction sends a request to Vizier, and saves the returned VOtable file under the name “vizier.xml”
astrometry.send_query_vizier(catalog, position, conesize, constraint)
The filename may be changed, as follows:
astrometry.send_query_vizier(catalog, position, conesize, constraint, filename = "data.xml")
Then the second instruction opens the file, and convert it to a Numpy record array. Numpy record arrays are special arrays that allow to store columns with different data type, with a name and format for each column. They are discussed here for instance.
stars = astrometry.read_votable("vizier.xml")
The name of the columns can be obtained with:
print stars.dtype.names
And the data in a given column:
print stars['column name']
Retrieving data from SkyBoT¶
Sending queries to SkyBoT is pretty much the same. An example of script is given below:
from aspylib import astrometry
#------ retrieving information from SkyBoT ------
date = 2455923.0
position = [56., 24.] #[alpha, delta] in degrees
conesize = [30., 30.] #[boxsize_alpha, boxsize_delta] in arcmin
astrometry.send_query_skybot(date,position,conesize)
cat = astrometry.read_votable("skybot.xml")
#------ printing information --------------------
print
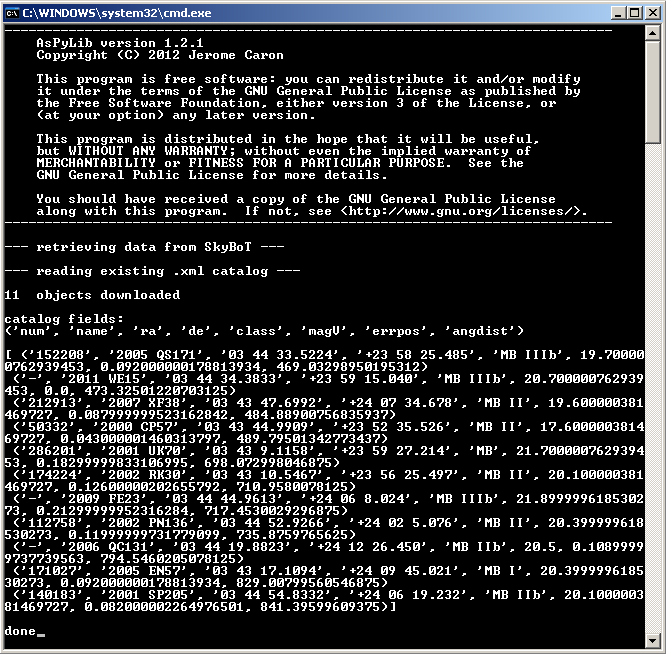
print len(cat)," objects downloaded"
print
print "catalog fields:"
print cat.dtype.names
print
print cat
print
raw_input("done")
Then the following messages are printed in the Python console:
More information¶
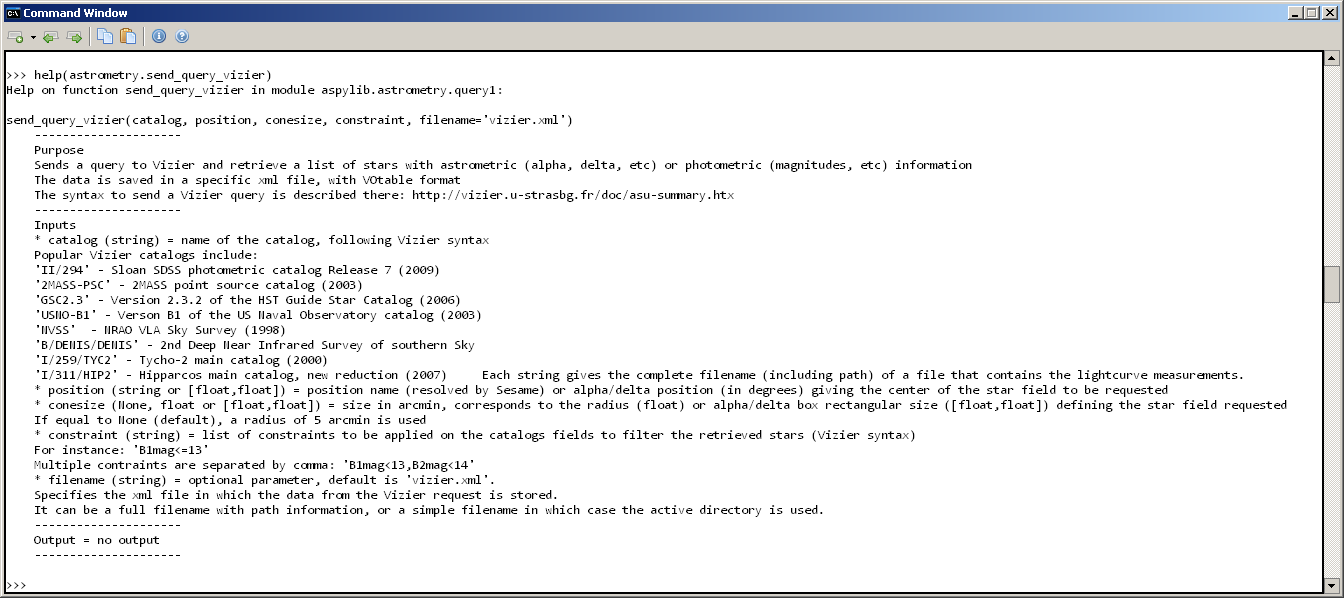
Getting more information about the AsPyLib functions is quite easy thanks to the console help. Just by typing this:
help(astrometry.send_query_vizier)
we get the following: